What is a Cantilever Scaffolding and Its Uses in Construction

Introduction
Cantilever scaffolding, also known as needle scaffolding, is a highly specialised access option for construction and maintenance jobs. It stretches horizontally from a structure, offering secure platforms across obstructions or gaps, in contrast to conventional ground-supported scaffolds.
This makes cantilever scaffolding especially useful when regular erection is impractical owing to site constraints or building design. Properly set up mobile scaffolding can complement cantilever scaffolding in areas where mobility and flexibility are required for safe access.
Cantilever Scaffolding
Cantilever scaffolding relies on beams or needles extending from a building wall to support raised work platforms. What is a cantilever? A cantilever is a rigid structural component that balances loads by counteracting moments. It is fixed at one end and free at the other.
Strong steel needles in scaffolding pass through wall apertures or rest on lower supports that are tightly braced to avoid tipping or wobbling. Platforms, guardrails, and toeboards round out the system for worker safety and compliance.
A typical cantilever scaffolding diagram shows fully decked platforms, needles extending 1.5–3 meters outward, and diagonal braces connecting levels for support. Cantilever support requires high-quality materials, such as Grade 43 steel tubes and rated couplers, to securely withstand working loads of 2-4 kN/m² during construction phases.
How it Works
Cantilever scaffolding uses load transfer and anchored extension to function. Needles (150-200mm diameter steel tubes) are inserted into pre-planned wall holes at 1.2-1.5m intervals and secured by back supports or trusses inside the building. These counteract the platform’s weight by sending forces to the stable floors or beams below.
The erection sequence ensures precision: engineers examine the site for load routes and wall capacity; base frames are secured to concrete slabs; needles are aligned plumb with levels; platforms are installed completely without gaps; and edge protection is added last.
Proper scaffold assembly is crucial to maintain stability and safety. Ties every 4m² and cross-bracing prevent wind and vibration. Images of cantilever scaffolding frequently feature multi-lift configurations with separate ties, emphasising modular adaptability.
Dismantling is a step-by-step process that involves removing platforms first, then needles, then sealing penetrations with mortar. Frequent inspections are essential at heights over 10 meters to ensure there is no deformation or settling.
Key Benefits on Cantilever Scaffolding
Cantilever scaffolding has several practical advantages over ground-based alternatives:
- Overcomes Obstacles: Does not require ground preparation or road closures to cross streets, excavations, or machinery.
- Accesses Overhangs: Reaches soffits, balconies, and cornices where towers cannot expand.
- Time & Money are Saved: Compared with full-height scaffolds, it requires 30–50% less material, and rapid modular assembly reduces human resources, demonstrating how scaffolding speeds up building projects.
- Improves Stability: In wind or earthquake zones, wall-anchored systems perform better than freestanding ones.
- Versatile Reusability: Steel parts can be used across a variety of projects, reducing long-term costs.
Drawbacks include wall alterations (temporary holes) and engineering calculations for spans over 2m. The benefits outweigh the disadvantages in urban or limited areas.
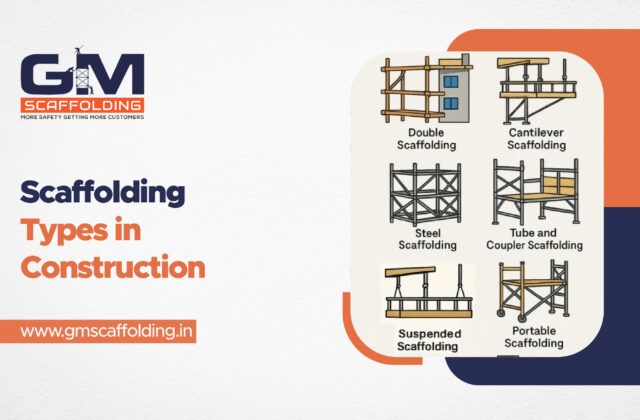
Common Types on Cantilever Scaffolding
Cantilever scaffolding adapts to needs through variations:
1.Single Cantilever (Basic Needle):
One needle row per lift supports light-duty tasks, such as painting or brick pointing, and projects 1-2m. Perfect for straightforward facades.
2.Double Cantilever Frame:
Parallel needle pairs with rakers increase capacity to 5 kN/m² for cladding or stone replacement. Improved for medium-heavy loads.
3.Counterbalanced Cantilever:
Cantilever support adds dead weight or backstays to the opposite platforms, making it suitable for weak walls or heritage buildings.
4.Rolling Cantilever Tower
Wheeled bases are ideal for guttering and linear maintenance since they allow for horizontal movement along elevations.
5.Truss-Out Cantilever:
These 4- to 6-meter-long triangulated steel beams support cranes or materials in stadium or bridge applications.
All incorporate standard components ledgers, transoms, and platforms for consistency and safety certification.
Related: https://blog.gmscaffolding.in/differences-between-cuplock-and-ringlock-scaffolding/
Applications
Cantilever scaffolding excels in specific scenarios:
- Maintenance for high-rise buildings includes parapet work above street level, spire painting, and chimney repairs.
- Building overhangs include cornice restoration, canopy margins and balcony undersides.
- Urban settings for uninterrupted facade access above traffic.
- Sloped terrain for higher elevations where the earth abruptly descends.
- Infrastructure: Water tank exteriors, bridge girders, and viaduct inspections.
Refurbishments
Use it for ornamental elements in industrial settings, such as silo chutes. For short-term requirements, scaffolding rental in Coimbatore offers certified cantilever scaffolding systems that comply with local regulations.
Related: https://blog.gmscaffolding.in/how-to-choose-right-scaffolding-rental-supplier/
Safety and Best Practices
Safety defines the success of cantilever scaffolding. Standards require complete planking, double guardrails above 2 meters, lift heights of 2 meters, bay widths of ≤2.4 meters, and toeboards. Independent ties every 4m² and outriggers for overhangs over 600mm. Shutdowns are necessary due to wind constraints of 12.5 m/s.
Competent erectors perform load tests, and daily tags indicate status (green: safe, red: out). Training includes harnesses, evacuation procedures, and no-change restrictions. Deflection is limited to span/300 by structural calculations.
Conclusion
Cantilever scaffolding bridges access gaps, allowing for safe work where other methods fail. From basic needles to truss-outs, its precision improves efficiency in building, maintenance, and repair. Proper planning, skilled workers, and thorough tests provide consistent performance, unlocking production on challenging sites.
FAQ
1.What is a cantilever, and how does it provide support in scaffolding?
A cantilever is a projecting structure with a fixed end that supports scaffolding platforms when ground support is not available.
2.What are the main benefits of using cantilever scaffolding in building projects?
It provides safe working locations at heights, reduces ground congestion, and permits access over obstructions.
3.What are the key components of cantilever scaffolding?
Main components include standards, ledgers, brackets, beams, platforms, braces, and secure anchorage points.
4.Where can I find cantilever scaffolding images or diagrams for reference?
Construction manuals, safety rules, and respected engineering or contractor websites can all provide you with valuable diagrams.
5.How is cantilever scaffolding installed safely on construction sites?
It is installed by skilled professionals who follow site safety regulations and use appropriate anchoring, load calculations, and inspections.